
Dr. Sanjay Barik
Knee & Shoulder Surgeon
Meet Our Doctor

Dr. Sanjay Barik
Orthopedic and Joint Replacement Surgeon
Dr. Barik's Orthocare Clinic
- MBBS
- MS - Orthopaedics
Meniscus Tear Knee Arthroscopy In Nagpur
A meniscal tear is an injury to the meniscus, the C-shape cartilage in the knee that acts as a cushion and provides stability and load distribution. This type of injury is often cause by twisting or rotating the knee, especially during times of stress. A meniscal tear can cause pain, swelling, and limited knee mobility.
Knee arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure commonly use to diagnose and treat meniscal tears. During arthroscopy, a small camera call an arthroscope is inserte through a small incision in the knee. This allows the surgeon to visualize the inside of the joint and determine the location and extent of the meniscal tear. Depending on the severity and type of tear, the surgeon uses small instruments to shorten, repair, or remove the damaged portion of the meniscus. Knee arthroscopy is preferred because it is less invasive, has a faster recovery time, and causes less postoperative discomfort than traditional open surgery.
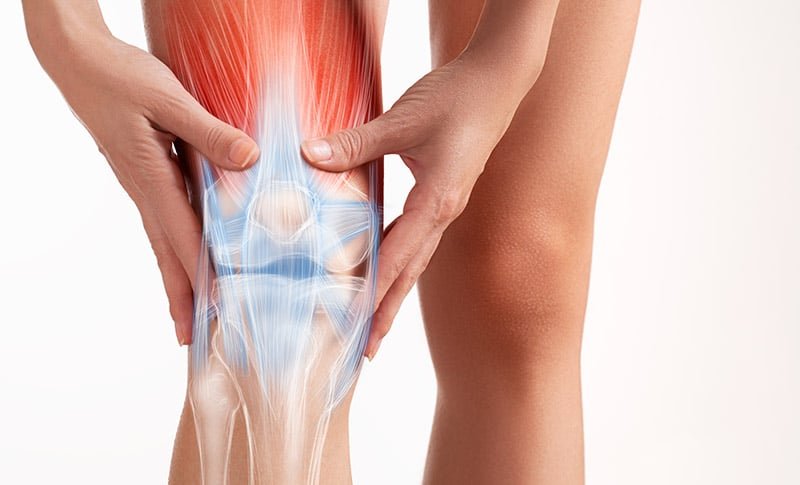
Symptoms of a Meniscal Tear
1. Pain: Persistent pain, especially along the knee joint line, is a common symptom. The intensity of the pain varies and may be worsene by certain movements.
2. Swelling: Knee swelling is a typical reaction to a meniscal injury. This swelling occurs immediately after the injury or arthroscopic surgery and may persist.
3. Stiffness: Your knee may feel stiff and you may have difficulty fully bending or straightening your leg. Stiffness is often more noticeable, especially after a period of inactivity.
4. Tightening or Locking Sensation: You may experience a catching or locking sensation in your knee, which prevents you from moving smoothly and without pain. This can occur when a torn meniscal fragment affects the movement of the joint.
5. Popping Sound: Some people with meniscal injuries may hear or feel a popping or clicking sound in their knee, especially when they move.
6. Decreased range of motion: Decreased range of motion in the knee, such as difficulty fully extending or bending the leg, is a common symptom.
6. Weakness: There may be weakness in the affected leg or instability that makes it difficult to bear weight or perform certain activities.
Goals of Arthroscopic Meniscal Repair
Firstly, The goal of meniscal surgery is to preserve healthy meniscal tissue. Thus, If the meniscus is torn, it needs a blood supply to heal.However, Only the outer third of the meniscus has a blood supply to help heal the tear. Repair is usually limited to this peripheral area of the meniscus.
Similarly, Many types of meniscal tears occur in areas of the meniscus that do not have sufficient blood supply for healing. For tears in the meniscal area without a blood supply, a meniscectomy is usually recommended.
Who should consider arthroscopic meniscal repair?
Thus, Recovery from meniscal repair takes longer than meniscectomy, but as a general rule, repairable menisci should be repaire. there is. Meniscal repair is considere when:
- the patient is healthy and wants to remain active,
- the patient understands rehabilitation and accepts the risks of surgery,
- the meniscal tear is locate around the meniscus. The
- meniscal tissues are of good quality and the
- surgeons have experience in meniscal repairs.
Procedure of Meniscus Tear Knee Arthroscopy in Nagpur
1. Anesthesia
Arthroscopic meniscal repair can be safely perform under general or spinal anesthesia. Therfore, In addition, a local anesthetic will be injecte into the knee and the incision site.Thus, Patients are encourage to discuss their preferences with their anesthesiologist prior to surgery.
2. Arthroscopic Meniscal Repair Time
Arthroscopic Meniscal Repair typically takes 1 to 1.5 hours. The time may be slightly longer or shorter depending on how many additional surgeries are needed to treat other knee problems.
3. Pain and Pain Management
Arthroscopic meniscal repair is moderately painful. It is more painful than standard arthroscopy because more soft tissue surgery is performed, but it is less painful than ligament reconstruction or another surgery that requires drilling holes in the bone. A local anesthetic will be used during the surgery to minimize pain. However, during the first three days after surgery, patients usually experience swelling and pain in the knee, which can be treated with oral anesthetics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
4. Taking Medications
Once, Oral anti-inflammatory drugs are taken orally according to a schedule, and narcotic analgesics are taken orally as needed. Patients require narcotic analgesics on average 2 to 5 days after surgery.
5. Effectiveness of Medications
Combining narcotic and anti-inflammatory analgesics provides highly effective analgesia with minimal side effects. Proper pain control requires a balance between effectiveness and side effects.Firstly, All narcotic painkillers can cause nausea and constipation, so drinking plenty of fluids and taking stool softeners after surgery can help alleviate these problems.


